Climate change refers to the long-term alteration of Earth’s average weather patterns.
It is a pressing issue that poses a significant threat to our planet and its inhabitants.
This blog post explores the complex interplay of factors that lead to climate change, including its scientific foundations, far-reaching effects, and the pressing need for coordinated action.
We hope to shed light on this critical issue and inspire readers to contribute to ongoing efforts to mitigate its impact by investigating the scientific mechanisms behind climate change, the consequences it imposes on our planet, and the global actions being taken.
Table of Contents
The Science Behind Climate Change
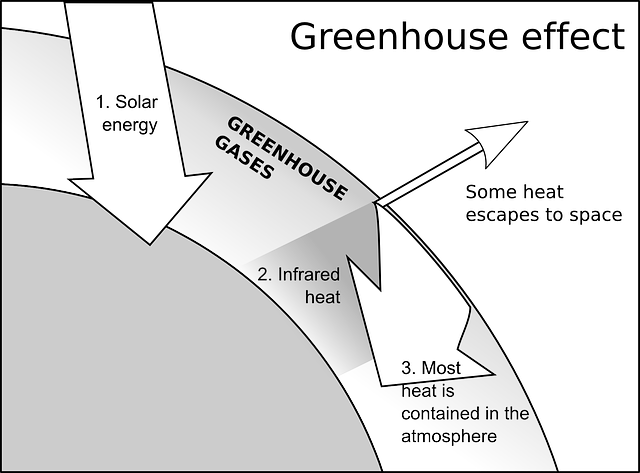
Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
The Earth’s atmosphere contains greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), which trap heat from the sun.
This natural process keeps our planet warm enough to sustain life.
However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly increased the concentration of these gases, intensifying the greenhouse effect.
This enhanced greenhouse effect leads to global warming, causing a rise in average global temperatures.
Role of Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Carbon dioxide, primarily emitted from activities like burning coal, oil, and natural gas for energy, is a major contributor to climate change.
These emissions create a thickening blanket of CO2 in the atmosphere, trapping more heat and leading to a rise in Earth’s temperature.
The excessive CO2 levels also lead to ocean acidification, endangering marine life and ecosystems.

Impact on Weather Patterns and Natural Disasters
Climate change disrupts established weather patterns, leading to an increase in extreme weather events.
This includes more intense hurricanes, prolonged droughts, heatwaves, and heavy rainfall, which can result in devastating floods and landslides.
Changes in weather patterns also affect agriculture, water resources, and human settlements, posing significant challenges to communities around the world.
Understanding these scientific principles is essential to grasping the severity of climate change.
The rising global temperatures, attributed to the intensified greenhouse effect, underscore the urgent need for decisive action to curb carbon emissions and mitigate the associated risks.

Consequences of Climate Change
Rising Global Temperatures
One of the most immediate and noticeable effects of climate change is the rise in global temperatures.
Average temperatures on Earth have increased significantly over the past century, with each subsequent decade being warmer than the last.
This warming trend accelerates the melting of polar ice caps, contributing to rising sea levels and threatening coastal communities.

Melting Polar Ice Caps and Rising Sea Levels
The warming climate accelerates the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps in Antarctica and Greenland.
As these vast ice masses melt, they contribute to rising sea levels, posing a grave threat to low-lying coastal areas and islands.
Rising sea levels lead to coastal erosion, loss of habitat for plants, animals, and humans, and an increased risk of flooding during high tides and storms.

Loss of Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Climate change disrupts ecosystems and threatens biodiversity.
Many plant and animal species are sensitive to changes in temperature and weather patterns, leading to shifts in habitats and potential extinction.
Coral reefs, vital marine ecosystems, are particularly vulnerable to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification, endangering the countless species that rely on them for survival.

Threats to Agriculture and Food Security
Changing climate patterns affect agricultural productivity.
Unpredictable weather conditions, altered rainfall patterns, and an increased frequency of extreme events like droughts and floods jeopardize crop yields and livestock production.
This instability in the agricultural sector threatens global food security, leading to potential food shortages and economic challenges, particularly in developing countries.

Economic Impacts
The consequences of climate change have far-reaching economic implications.
Disasters related to climate change, such as hurricanes, wildfires, and flooding, cause billions of dollars in damages each year.
Additionally, the impact on industries like agriculture, tourism, and fisheries can lead to job losses and economic instability.
Furthermore, the costs of adapting to a changing climate, such as building resilient infrastructure, also strain national economies.
These consequences underscore the urgent need for global cooperation to mitigate climate change.
Addressing these challenges requires immediate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect vulnerable ecosystems, and build resilience in communities to safeguard against the impacts of a warming planet.

Human Activities Contributing to Climate Change
Fossil Fuel Consumption
The burning of fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, for energy is the largest contributor to human-induced greenhouse gas emissions.
Industries, transportation, and electricity generation heavily rely on these fossil fuels.
The combustion process releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, amplifying the greenhouse effect and driving global warming.

Deforestation
Deforestation, the large-scale clearing of forests for agriculture, urban development, and logging, disrupts the natural balance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Trees act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 during photosynthesis.
When forests are cleared, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere, contributing to increased greenhouse gas concentrations.
Deforestation also leads to the loss of biodiversity and disrupts local and global climate patterns.

Industrial Emissions
Industrial processes, such as manufacturing, chemical production, and mining, release various greenhouse gases, including methane and nitrous oxide, into the atmosphere.
These emissions occur during activities like cement production and chemical manufacturing.
Methane, in particular, is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release significantly contributes to global warming. Controlling industrial emissions is essential to mitigating climate change.

Agriculture and Livestock Farming
Agriculture contributes to climate change through practices such as livestock farming and rice cultivation.
Livestock, particularly cattle, produce methane during digestion, which is released into the atmosphere.
Additionally, agricultural activities can lead to soil degradation and the loss of soil carbon.
Deficient soil management practices can also release nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
Sustainable agricultural practices are key strategies to mitigate these emissions.
Addressing these human-induced activities is crucial in the fight against climate change.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, conserving forests, and implementing green technologies are essential steps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and creating a more sustainable future for our planet.

Global Efforts to Combat Climate Change
The Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015 under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), is a landmark international treaty.
Its goal is to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, with an ambition to limit the increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Countries that are parties to the agreement have committed to reducing their greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing adaptation efforts, and providing financial assistance to developing nations to cope with climate change impacts.

Renewable Energy Initiatives
The shift toward renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power, plays a pivotal role in mitigating climate change.
Governments and private organizations worldwide are investing in renewable energy projects to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Advancements in technology have made renewable energy more accessible and affordable, making it a viable alternative and a significant contributor to reducing carbon emissions.

Sustainable Development Goals
Climate action is a core component of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Goal 13, “Climate Action,” emphasizes the urgent need to take meaningful steps to combat climate change and its impacts.
Efforts to achieve this goal include raising awareness, building capacity for climate mitigation and adaptation, and integrating climate change measures into national policies and planning processes.

Role of International Organizations and Governments
International organizations, such as the United Nations and the World Bank, work in collaboration with governments to address climate change.
They provide funding, technical expertise, and policy guidance to support climate initiatives globally.
Additionally, many national governments have introduced regulations and policies to promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices in various sectors of the economy.
These global efforts reflect the collective determination to combat climate change.
Collaboration between nations, supported by international agreements and initiatives, is essential to creating a sustainable future.
By working together and implementing comprehensive strategies, the world can move closer to achieving the goals set forth in the Paris Agreement and making significant progress in mitigating the impacts of climate change.

Individual and Community Actions
Energy Conservation
Individuals can contribute to mitigating climate change by conserving energy in their homes and workplaces.
Simple actions such as using energy-efficient appliances, switching to LED lighting, and properly insulating buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Additionally, being mindful of energy use by turning off lights and electronics when not in use can make a difference in reducing carbon emissions.

Reducing, Reusing, and Recycling
Adopting a lifestyle focused on reducing, reusing, and recycling can minimize the environmental impact.
By reducing single-use plastic and opting for reusable products, individuals can decrease the demand for resource-intensive manufacturing processes.
Recycling materials like paper, glass, and plastic helps conserve resources and reduces the energy required for producing new items.

Supporting Renewable Energy Sources
Consumers can support the transition to renewable energy by choosing green energy options provided by utilities.
Many regions offer renewable energy programs that allow individuals to source electricity from wind, solar, or other clean sources.
By supporting these initiatives, individuals contribute to the growth of renewable energy infrastructure and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.

Advocacy and Climate Activism
Engaging in climate advocacy and activism is crucial for raising awareness and driving policy changes.
Individuals can participate in local environmental organizations, attend climate-related events, and advocate for climate-friendly policies at the community and national levels.
Social media platforms provide avenues for sharing information and mobilizing public support for climate action.
Empowering individuals and communities to take meaningful actions against climate change is essential.
By adopting sustainable practices, promoting environmental awareness, and advocating for policy changes, people can collectively contribute to the global efforts aimed at mitigating climate change.
Through these actions, individuals not only reduce their own carbon footprint but also inspire others to join the movement toward a more sustainable future.


Challenges and Obstacles
Political and Corporate Interests
One of the significant challenges in combating climate change is the resistance from political and corporate interests.
Industries heavily reliant on fossil fuels often resist regulations and policies aimed at reducing emissions due to economic concerns.
Political lobbying and campaign funding from these industries can hinder the implementation of effective climate policies, delaying necessary actions to address the issue.
Lack of Awareness and Education
Limited awareness and understanding of climate change pose a significant obstacle.
Many individuals are unaware of the severity of the issue, its causes, and potential solutions.
Education and awareness campaigns are essential to inform the public about climate change, its consequences, and the actions needed to mitigate it.
Without widespread understanding, it is challenging to mobilize public support for climate initiatives.


Technological and Financial Barriers
Developing and implementing clean technologies requires significant investment and research.
Many developing countries face financial constraints, making it difficult for them to adopt renewable energy solutions and other climate-friendly technologies.
Additionally, the lack of access to advanced technologies hampers efforts to reduce emissions and adapt to changing climate conditions, especially in vulnerable regions.
Overcoming these challenges requires coordinated efforts from governments, businesses, and civil society.
Addressing political and corporate resistance, improving education and awareness, and providing financial and technological support to developing nations are crucial steps in overcoming these obstacles and advancing the global fight against climate change.
By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, the international community can work together to create a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
Conclusion
From rising global temperatures and melting polar ice caps to threats to biodiversity and agriculture, the impacts of climate change are vast and urgent.
The evidence presented underscores the critical need for immediate action.
Every individual, community, and nation play a role in addressing this global crisis.
By reducing carbon emissions, conserving energy, supporting renewable technologies, and advocating for climate-friendly policies, we can collectively work towards a more sustainable future.
It is essential to hold governments and corporations accountable and demand bold, decisive action to combat climate change.
Despite the challenges, there is hope.
The global community has made strides in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and climate awareness.
The Paris Agreement and other international efforts demonstrate a collective commitment to change.
By building on these initiatives and fostering a sense of urgency, we can mitigate the worst effects of climate change and create a world where future generations can thrive.
I remember learning about the ozone layer in elementary school in the 1980s.
Do kids still learn about the environment in elementary school nowadays?

