In today’s digital age, where privacy concerns and online security threats are rampant, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as essential tools for internet users.
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that enables a secure and encrypted connection over the internet, offering users a shield against cyber threats and unauthorized access to their data.
As we delve into the intricacies of VPNs, it becomes evident that these tools play a crucial role in safeguarding our online presence and ensuring a more secure browsing experience.
The significance of online privacy and security cannot be overstated.
With a growing number of cyberattacks, data breaches, and privacy infringements, individuals are seeking effective ways to protect their sensitive information.
This is where VPNs come into play, offering a robust solution to enhance the security of internet connections and empower users to navigate the online realm with confidence.
Let’s explore the workings of VPNs, their various applications, and the factors to consider when choosing the right VPN for your needs.
Table of Contents
How VPNs Work
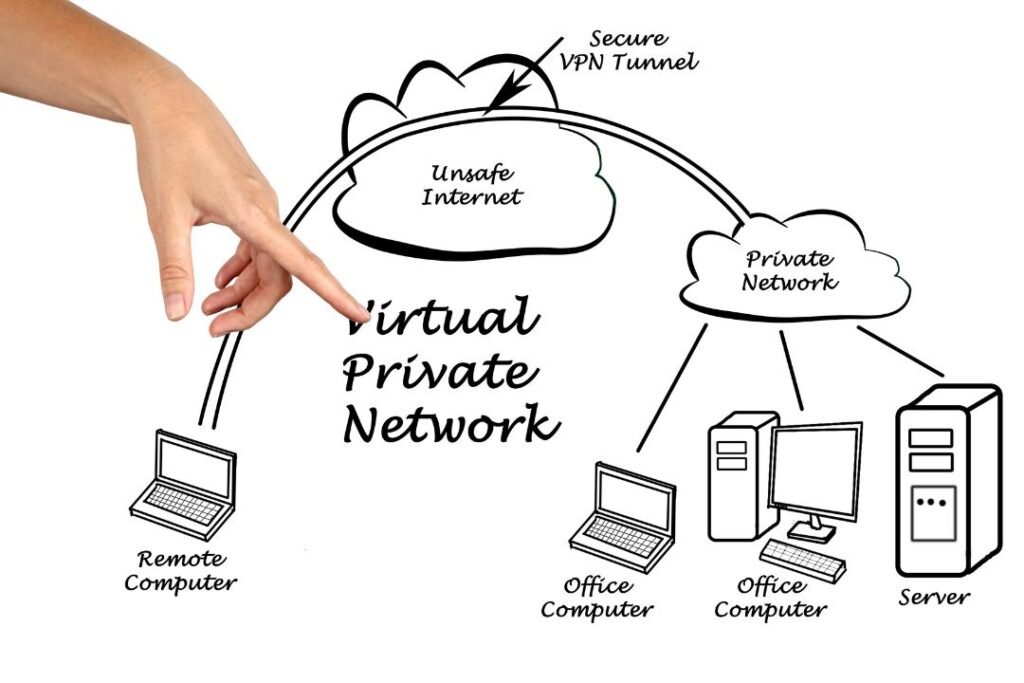
A. Encryption
VPNs employ advanced encryption techniques to secure the data transmitted between a user’s device and the VPN server.
This process involves encoding the information in such a way that even if intercepted, it remains unreadable without the corresponding decryption key.
Common encryption protocols include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, and IKEv2/IPsec, each with its own strengths and use cases.
B. Tunneling
The concept of “tunneling” is fundamental to VPN functionality.
When a user connects to a VPN, their data is encapsulated within a secure tunnel, which acts as a protective conduit through the internet.
This tunnel shields the transmitted data from potential threats, ensuring that it remains confidential and intact during transit.
The choice of tunneling protocols, such as PPTP, L2TP, or SSTP, influences the performance and security of the VPN connection.
C. IP Masking
VPNs mask the user’s real IP address by assigning a temporary one from the VPN server’s pool.
This process enhances privacy and anonymity, making it challenging for websites, advertisers, or malicious entities to trace a user’s online activities back to their actual location.
IP masking is particularly valuable for bypassing geo-restrictions, allowing users to access content or services that may be limited to specific regions.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of VPN operation sheds light on how these tools create a secure environment for online activities.
Encryption, tunneling, and IP masking collectively contribute to the robust protective barrier that VPNs offer, emphasizing the importance of these technologies in safeguarding sensitive information in the digital landscape.
Reasons to Use a VPN

A. Enhanced Security on Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks, often found in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, are susceptible to security risks.
Hackers can exploit these unsecured connections to intercept data transmitted by users.
VPNs provide a crucial layer of security by encrypting the data, making it significantly more challenging for unauthorized parties to access sensitive information such as login credentials or personal details.
B. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Content availability varies across regions due to licensing agreements, leading to frustrating limitations for users.
VPNs enable individuals to virtually relocate by connecting to servers in different countries.
By doing so, users can bypass geo-restrictions imposed on content, accessing websites, streaming services, or online resources as if they were in the server’s location.
This functionality broadens access to a global internet experience.
C. Anonymous Browsing
VPNs contribute to online anonymity by masking users’ IP addresses and encrypting their internet traffic.
This protects against potential surveillance and shields users from invasive tracking by advertisers and other online entities.
Anonymous browsing ensures a more private online experience, reinforcing the user’s control over their digital footprint and reducing the risk of targeted advertisements or data profiling.
Understanding the diverse reasons for using a VPN emphasizes the versatility of these tools.
From enhancing security on public networks to unlocking global content and preserving online anonymity, VPNs serve as multifaceted solutions for users seeking a safer and more unrestricted online experience.
Types of VPNs

A. Remote Access VPNs
1. Definition: Remote access VPNs allow individual users to connect securely to a private network from a remote location, typically over the internet.
This is ideal for employees working from home or on the go, granting them secure access to company resources as if they were physically present in the office.
2. Implementation: Remote access VPNs often utilize encryption protocols like SSL/TLS or IPsec to establish a secure connection.
Users typically need VPN client software or apps to initiate the connection.
B. Site-to-Site VPNs
1. Definition: Site-to-site VPNs connect entire networks rather than individual devices.
They are commonly used by businesses with multiple locations, linking geographically dispersed offices into a unified network.
This facilitates seamless communication and resource sharing between different branches.
2. Implementation: Site-to-site VPNs establish a secure “tunnel” between the routers or firewalls of the connected networks.
This tunnel is encrypted, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted between the sites.
C. Client-to-Server VPNs
1. Definition: Client-to-server VPNs, also known as consumer VPNs, are the most common type used by individual users.
These VPNs enable a single device (client) to connect securely to a VPN server, typically managed by a third-party VPN service provider.
2. Implementation: Users install VPN client software or apps on their devices, allowing them to connect to worldwide servers.
These VPNs often offer various encryption protocols and server locations to cater to user preferences and specific needs.
Understanding the distinctions between these types of VPNs provides insight into their varied applications.
Whether for individual privacy, corporate network connectivity, or interconnecting multiple locations, the versatility of VPNs makes them essential tools for addressing different security and accessibility requirements.
Choosing the Right VPN

A. Consideration of Security Protocols
1. Encryption Standards: Evaluate the encryption protocols offered by VPN services.
Common options include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, IKEv2/IPsec, and PPTP. Opt for services that prioritize robust encryption to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of your data.
2. Protocol Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the encryption protocols with your devices and operating systems.
A VPN that supports a variety of protocols provides flexibility in adapting to different platforms.
B. Server Locations
1. Global Coverage: Assess the geographical distribution of a VPN provider’s servers.
A diverse range of server locations allows users to access content from different regions and can contribute to better performance.
2. Server Numbers: Higher server counts often correlate with better performance and reduced congestion.
More servers also enhance the likelihood of finding a server that meets specific needs, such as low-latency gaming or high-bandwidth streaming.
C. Logging Policies
1. No-Logs Policy: Prioritize VPN services with a strict no-logs policy, meaning they do not store user activity or connection data.
This ensures a higher level of privacy by minimizing the potential for data exposure.
2. Privacy Transparency: Look for VPN providers that are transparent about their privacy practices.
Clear and concise privacy policies help users understand how their data is handled and stored.
Selecting the right VPN involves careful consideration of these factors.
By prioritizing robust security protocols, extensive server coverage, and transparent logging policies, users can make informed choices that align with their specific privacy and accessibility requirements.
Setting Up a VPN
Step-by-step Guide
1. Choose a VPN Service: Begin by selecting a reputable VPN service that aligns with your security and privacy needs. Consider factors such as encryption protocols, server locations, and user reviews.
2. Sign Up: Register for an account with your chosen VPN provider. This often involves providing an email address and creating a secure password.
3. Download and Install the VPN App: Most VPNs offer dedicated applications for various devices and operating systems. Download the app from the official website or app store and follow the installation instructions.
Popular VPN Services
1. ExpressVPN: Known for its high-speed servers and strong security features, ExpressVPN offers a user-friendly interface and a vast server network.
2. NordVPN: Renowned for its robust security measures, NordVPN provides a large server network and specialty servers for specific activities like streaming or P2P file sharing.
3. Surfshark: Recognized for its unlimited simultaneous connections, Surfshark offers a budget-friendly option without compromising on security features.
4. Proton VPN: Known for its commitment to privacy, its open-source software, and its support for censorship-resistant internet. Proton VPN also has features like Secure Core servers, Kill Switch, Adblocker, and Split Tunneling to enhance your security and flexibility.
Connecting to a VPN
1. Launch the VPN App: Open the installed VPN application on your device.
2. Log in: Enter your login credentials to access the VPN service.
3. Select a Server: Choose a location based on your preferences or specific needs, such as accessing region-restricted content or optimizing for speed.
4. Connect: Click the connect button to establish a secure VPN connection. Once connected, your internet traffic is encrypted and routed through the selected server.
By following these steps and utilizing reputable VPN services, users can enhance their online security, access geo-restricted content, and enjoy a more private browsing experience.
The simplicity and effectiveness of VPN setup make it a practical solution for individuals seeking to bolster their digital privacy.
Common VPN Myths

A. Unlimited Anonymity
1. Myth: Using a VPN ensures complete online anonymity.
2. Reality: While VPNs significantly enhance privacy, they don’t provide absolute anonymity. Users should be aware of other privacy measures and potential vulnerabilities, such as DNS leaks or browser fingerprinting.
B. Slow Internet Speed
1. Myth: VPNs always result in slower internet speeds.
2. Reality: While a slight decrease in speed is common due to encryption and routing through VPN servers, many modern VPNs offer high-speed connections.
Choosing servers strategically and using a reputable VPN service can minimize speed loss.
C. Only for Tech-Savvy Users
1. Myth: Setting up and using a VPN is too complex for the average user.
2. Reality: Many VPNs offer user-friendly interfaces and straightforward installation processes. Most users can easily navigate VPN apps without requiring advanced technical knowledge.
Dispelling these common myths is crucial for users to make informed decisions about VPN use.
Understanding the realities behind these misconceptions ensures that individuals can leverage VPN technology effectively while avoiding unrealistic expectations.
VPNs and Net Neutrality

A. Ensuring an Open Internet
1. Importance of Net Neutrality: Net neutrality advocates for equal treatment of all internet traffic, preventing internet service providers (ISPs) from favoring or throttling specific websites or services.
2. VPNs as a Safeguard: VPNs play a role in preserving net neutrality by encrypting users’ internet traffic. This encryption makes it challenging for ISPs to inspect and selectively control or limit the speed of certain online activities.
B. Impact on Online Freedom
1. Counteracting Censorship: In regions where internet censorship is prevalent, VPNs empower users to bypass restrictions and access a more open internet.
By connecting to servers in different countries, users can circumvent government-imposed limitations on content and communication.
2. Supporting Freedom of Expression: VPNs contribute to the protection of freedom of expression by allowing users to share information without fear of censorship or surveillance.
Journalists, activists, and individuals in oppressive regimes often rely on VPNs to communicate securely and access unbiased information.
Understanding the relationship between VPNs and net neutrality underscores the broader implications of these tools beyond personal privacy.
By facilitating unrestricted access to information and countering censorship, VPNs become essential tools in upholding the principles of a free and open internet
Challenges and Risks

A. Potential for Misuse
1. Privacy Concerns: While VPNs are designed to enhance privacy, there’s a potential for misuse.
Some individuals may exploit VPNs for illicit activities, making it crucial for users to adhere to ethical guidelines and legal standards when utilizing these services.
2. Cybersecurity Threats: VPNs can be targeted by cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
Users must stay informed about potential threats, keep their VPN software updated, and choose reputable providers to minimize security risks.
B. Legal Implications
Different countries have varying regulations regarding the use of VPNs.
Users should be aware of and comply with local laws to avoid legal consequences.
Some countries restrict or ban VPN usage, emphasizing the importance of understanding the legal landscape.
C. VPN Service Reliability
1. Server Downtime: VPN services may experience occasional server downtimes or disruptions.
Users should consider the reliability of a VPN provider by researching their server uptime and response to technical issues.
2. Trustworthiness of Providers: Selecting a reputable VPN provider is crucial.
Users should be cautious of free VPN services that may compromise privacy or security in exchange for providing a no-cost service.
Opting for well-established, trustworthy providers can mitigate these risks.
Navigating the challenges and risks associated with VPN usage requires a balance between maximizing the benefits and being aware of potential pitfalls.
Users can mitigate these concerns by staying informed, adhering to legal standards, and making informed choices when selecting and using VPN services.
Conclusion
Recap of VPN Benefits
1. Privacy and Security: VPNs offer a robust layer of encryption, safeguarding users’ data from potential threats and unauthorized access, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
2. Access to Restricted Content: By masking IP addresses and allowing users to connect to servers in different regions, VPNs enable access to geo-restricted content, providing a more open and global internet experience.
3. Anonymity and Freedom: VPNs contribute to online anonymity, protecting users from tracking and surveillance. They play a crucial role in upholding freedom of expression, especially in regions with internet censorship.
Encouragement for Responsible VPN Use
1. Legal Compliance: Users should be aware of and comply with local laws regarding VPN usage to avoid legal implications.
2. Ethical Considerations: Responsible use of VPNs involves ethical considerations, including refraining from activities that may compromise privacy or violate legal standards.
3. Continuous Awareness: The digital landscape evolves, and users should stay informed about potential challenges, risks, and advancements in VPN technology.
In conclusion, VPNs stand as indispensable tools for individuals seeking to enhance their online privacy, security, and access to a globalized internet.

